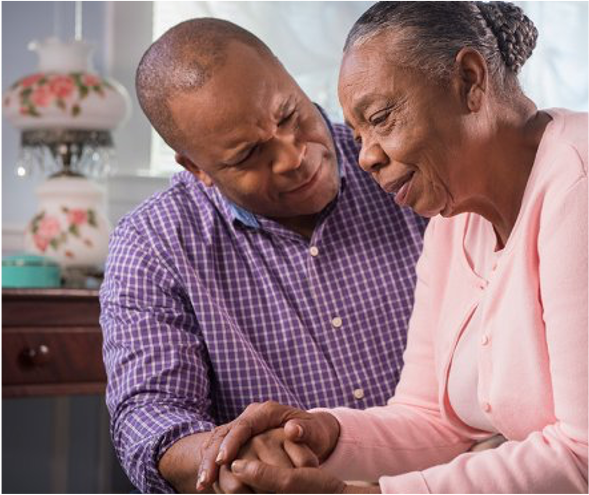
This year, the HTO research group has launched a seminar series on funding applications, led by Åsa Cajander, Sofia Ouhbi, and Jessica Lindblom. This initiative emerged from our annual strategic meeting, where we discuss the research group’s focus, future goals, targeted conferences, collaborations, and social events. A common theme that surfaced during these discussions was the need to strengthen our grant-writing skills, leading to the creation of this seminar series.
The series consists of six interactive seminars, where participants analyze both successful and unsuccessful funding applications. Our goal is to understand what makes an application stand out, recognize potential pitfalls, and refine our own grant-writing strategies. These sessions are designed to be inclusive and beneficial for everyone, from PhD students and postdocs to senior researchers, docents, and professors. Regardless of prior success in securing grants, there is always something new to learn. By engaging in discussions and sharing experiences, we aim to build a stronger, more confident research community equipped to navigate the competitive world of funding applications.
First Seminar on 23 January
Securing research funding in Sweden and the European Union is highly competitive. To help researchers navigate this landscape, the first seminar started with an overview of major funding opportunities. The first seminar introduced key funding agencies, including the Swedish Research Council (Vetenskapsrådet, VR), FORTE, FORMAS, AFA, VINNOVA, Horizon Europe, Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions (MSCA), the European Research Council (ERC), and WASP-HS.
Understanding The Funding Landscape
The seminar was attended by over 20 participants, including PhD students, postdocs, researchers, docents, and senior professors. To foster engagement, we began with an icebreaker session, where participants introduced themselves and shared their experiences with funding applications.
Led by Prof. Cajander, the session provided a comparative analysis of different funding bodies, focusing on:
- Their core priorities and evaluation criteria
- The types of projects they tyoically fund
- Key factors that make applications successful
In addition to major grants, we also discussed travel grants for doctoral students and funding opportunities available at the university and national levels.
This was followed by an interactive discussion where attendees reflected on key takeaways. The session provided valuable insights into how to tailor applications for different funding bodies and maximize the chances of success.
Academic Credit Opportunity for PhD Students
PhD students have the possibility to earn academic credits if they attend at least five out of six seminars and actively participate in discussions. This is in discussion with their PhD supervisor. This ensures that participants engage deeply with the material while gaining practical skills in grant writing.
Second Seminar on 25 February
In our second seminar, we explored the application process for FORTE funding by analyzing four real-life applications—three successful and one unsuccessful—along with their corresponding reviews. The session was divided into two parts: an informative presentation followed by group discussions.
Understanding FORTE’s Funding Landscape
The first half of the seminar featured a presentation by Sofia Ouhbi, who outlined the key focus areas of FORTE, the different types of calls, and the various application formats available. She also provided an analysis of the common characteristics of successful applications, offering valuable insights into what FORTE typically prioritizes in its funding decisions.
We were also joined by Magdalena Stadin, a postdoctoral researcher in human-computer interaction and a recipient of FORTE’s starting grant for postdocs. Having contributed to multiple successful FORTE applications, Magdalena shared her firsthand experience of the application process. She provided practical advice on approaching FORTE applications, highlighted key strategies, and emphasized the importance of persistence for early-career researchers.
Group Discussions and Reflections
In the second half of the seminar, Prof. Cajander, a FORTE board member, discussed the organization’s future plans and funding directions. Following this, participants were divided into three groups—doctoral students, postdocs, and senior researchers—to critically analyze the previously shared applications.
Each group examined the strengths and weaknesses of both successful and unsuccessful applications, identifying key takeaways and strategies for improvement. The discussions centered around best practices, common pitfalls to avoid, and essential elements to include in a strong FORTE application.
To conclude the seminar, the groups presented their reflections, sharing insights on how to craft more competitive funding applications. The session was facilitated by Prof. Cajander, ensuring a productive and engaging discussion. Overall, this seminar provided a deeper understanding of FORTE’s application process and valuable peer learning opportunities.
The key takeaway? Successful funding applications require a good idea, strategy, persistence, a good team, and a strong understanding of what the funding body values.
What’s Next?
On 25 March, we look forward to the next seminar which will focus on The Swedish Research Council (Vetenskapsrådet, VR). We meet at Theatrum Visuale at Ångström. Please write to Prof. Cajander if you wish to join.
Does this seem interesting? See you there!